Circuits are designed to handle a limited amount of electricity, and when too much current passes through, it can cause the wiring to overheat. This may damage vital electrical components, or even lead to fires. Switchgears are designed to defend equipment connected to a power supply from the threat of electrical overload.
Switchgear Definition
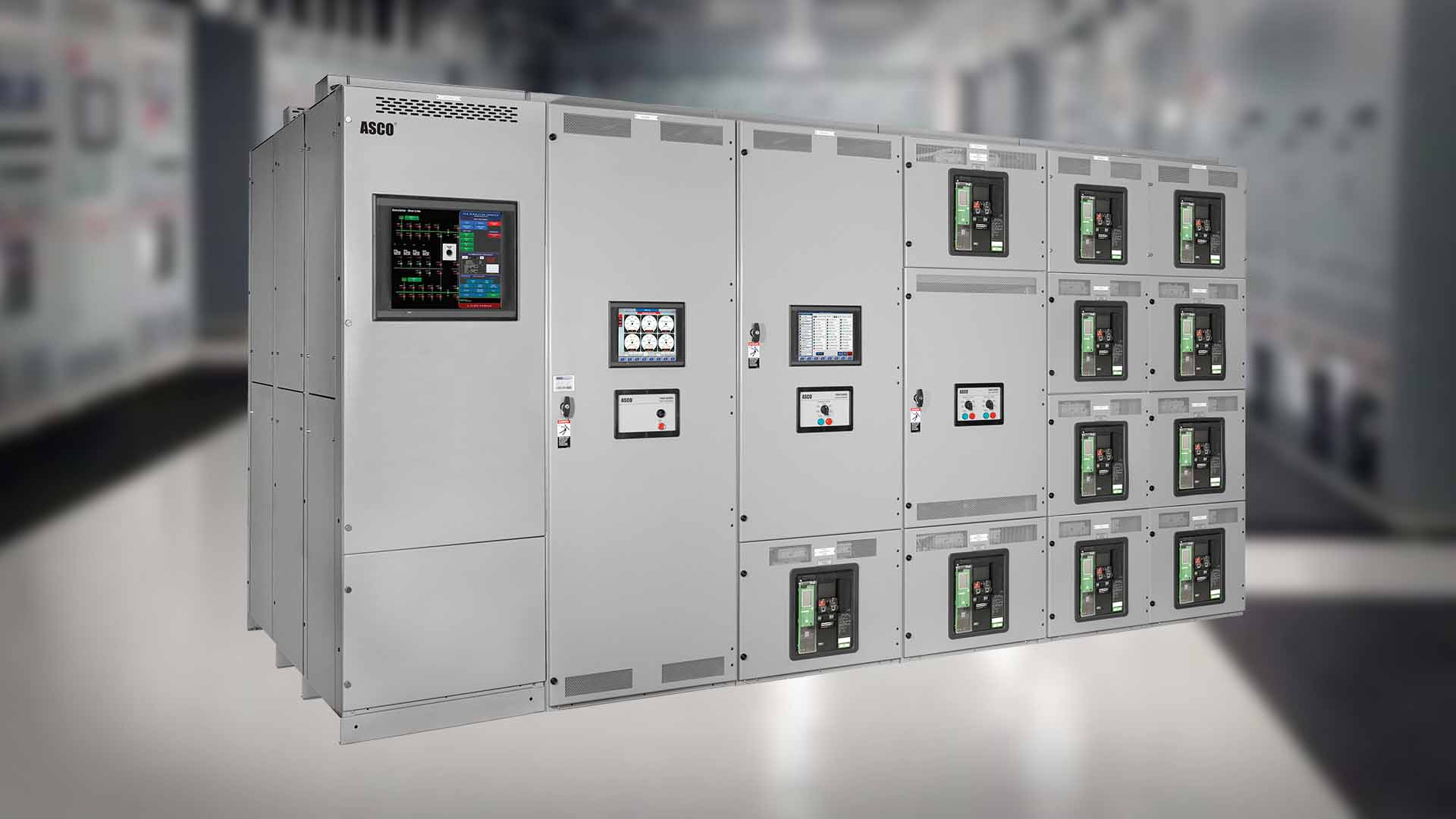
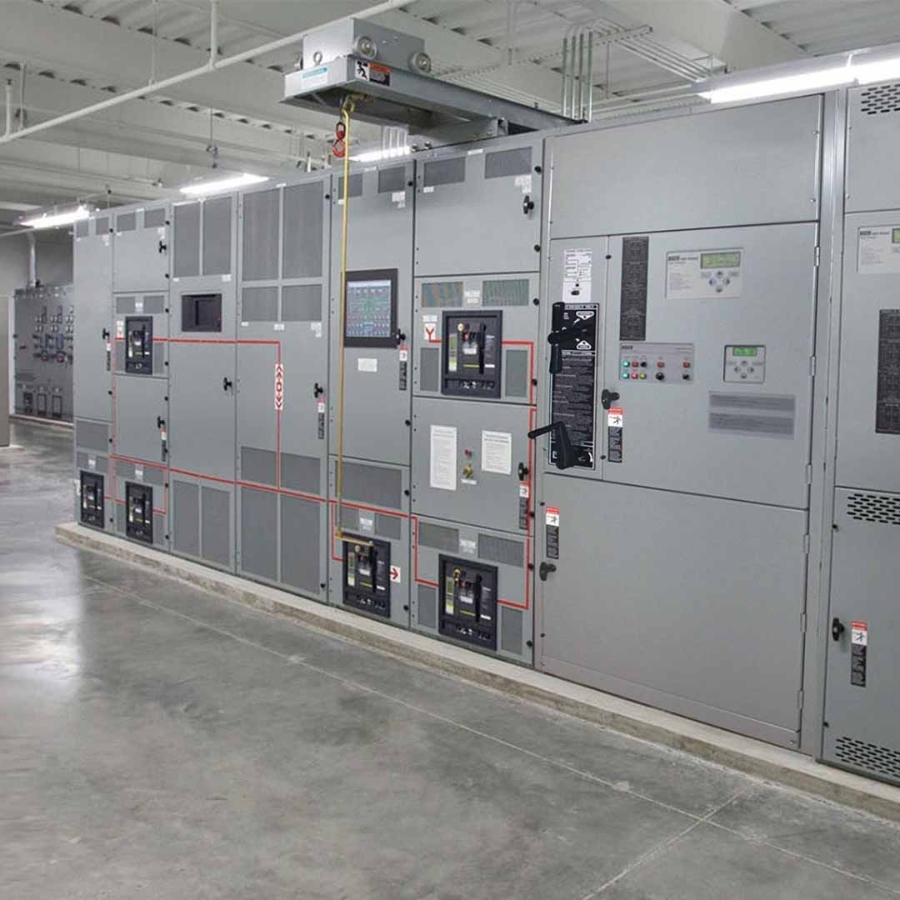
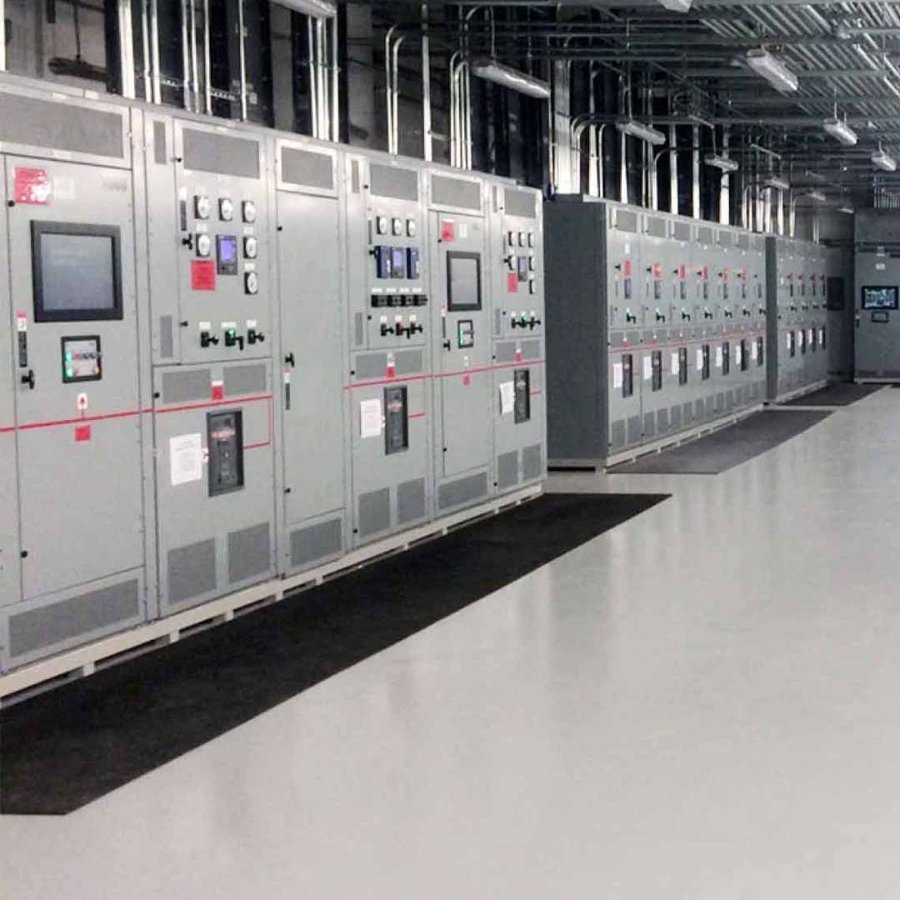
What is switchgear? Switchgear is a broad term that describes a wide variety of switching devices that all fulfill a common need: controlling, protecting, and isolating power systems. This definition can be extended to include devices to regulate and meter a power system, circuit breakers, and similar technology.
In the event of an electrical surge, an effective switchgear will trigger, automatically interrupting the flow of power and protecting the electrical systems from damage. Switchgears are also used for de-energizing equipment for safe testing, maintenance, and fault clearing.
Switchgear Examples
The term switchgear may refer to different systems and components. Switchgear examples include the following:
• Switches
• Fuses
• Isolators
• Relays
• Circuit Breakers
• Lightning Arresters
Switchgear types
There are three different classes of switchgear systems: low-voltage, medium-voltage, and high-voltage.
High-Voltage Switchgears
High-voltage switchgears are those that control 75KV of power or more. Because these breakers are designed for high-voltage use, they often include improved safety features.