Using Tie Breakers and Segmented Bus
Paralleling Switchgear Systems provide the highest levels of redundancy and maintainability for backup power applications. Understanding the function of tie breakers and electrical bus are key to optimizing backup power system configurations. The following sections describe tie breaker functions and provide examples of bus arrangements for a range of applications.
Overview of Breakers in Electrical Systems
Circuit breakers are used for multiple purposes in electrical systems. They are commonly used to connect electrical systems to power sources and to load circuits, and to protect people and equipment from overcurrents. On the source-side of electrical bus, generator breakers connect generators to electrical distribution bus, and utility main breakers connect electrical power feeds to bus. On the load side, distribution breakers connect and protect downstream loads, either directly or through automatic transfer switches.
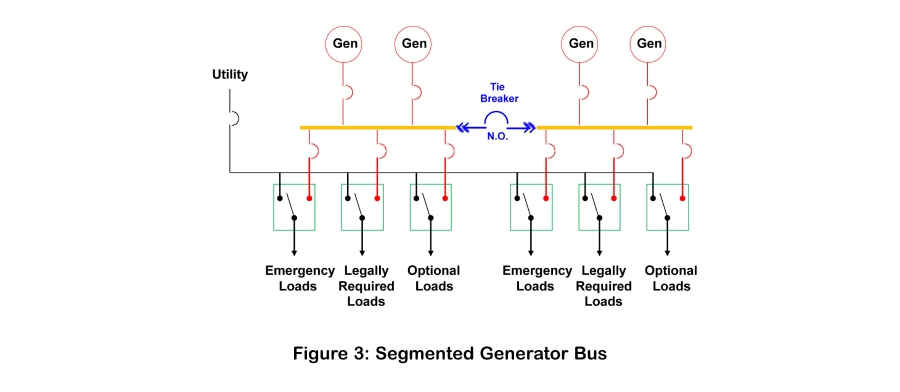
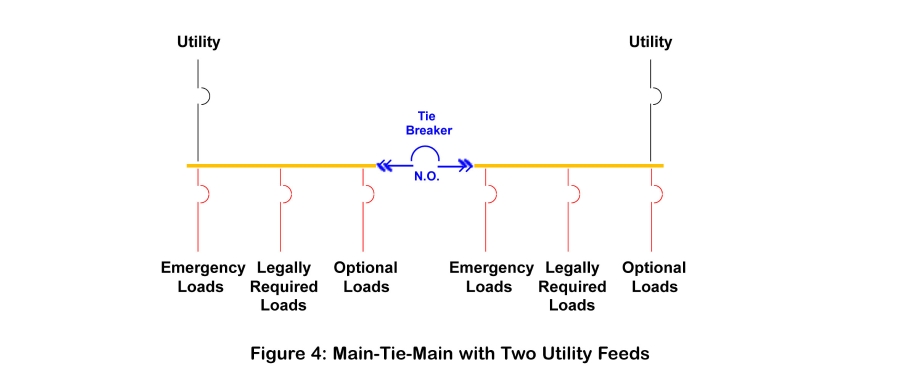
A Tie Breaker is a type of circuit breaker that connects two sections of electrical bus serving different power sources. When closed, current can pass in either direction between them. As a result, they enable various arrangements for connecting power sources to loads, including paralleling two dissimilar power sources. Although this is most often the intent of the term tie breaker, it is also less formally used to identify breakers placed between two sections of bus.
Tie breakers are commonly applied to backup power systems in two ways. A Tie circuit breaker, such as a Utility Bus Tie or a Generator Bus Tie, connects similar power sources. Separately, a Generator Main Breaker ties a generator bus to a load bus. In this location, it can be used to transfer load between a utility source and a generator source. It can also be used to isolate elements of the system to deenergize it for maintenance and repair of devices and their components.
For additional information on the types of breakers used in power systems, see the ASCO Technical Brief entitled Nomenclature for Low-Voltage Circuit Breakers.
Types of Bus
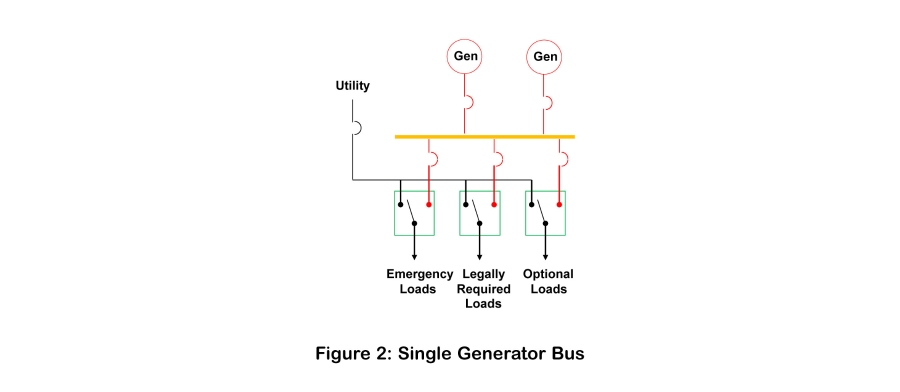
Electrical bus is named for the type of equipment it connects. Common Bus connects both power source and load circuits. Generator Bus connects only generators together, and Utility Bus does the same for two or more utility feeds.
Common Arrangements
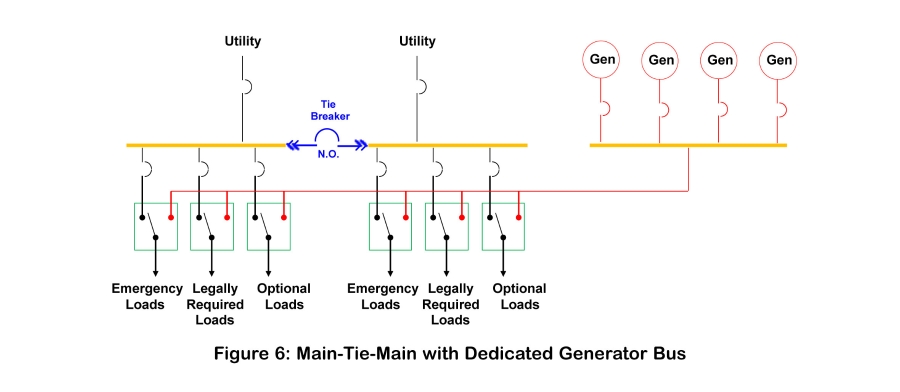
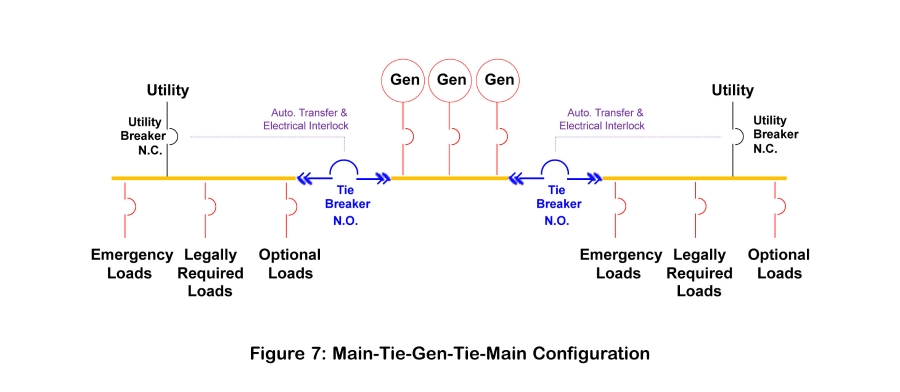
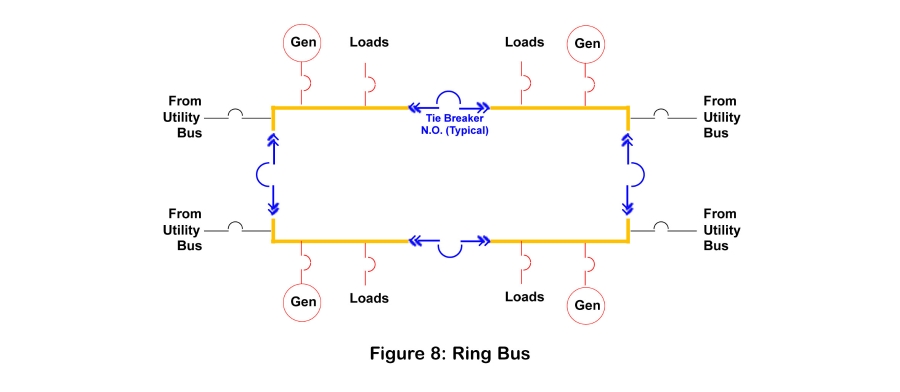
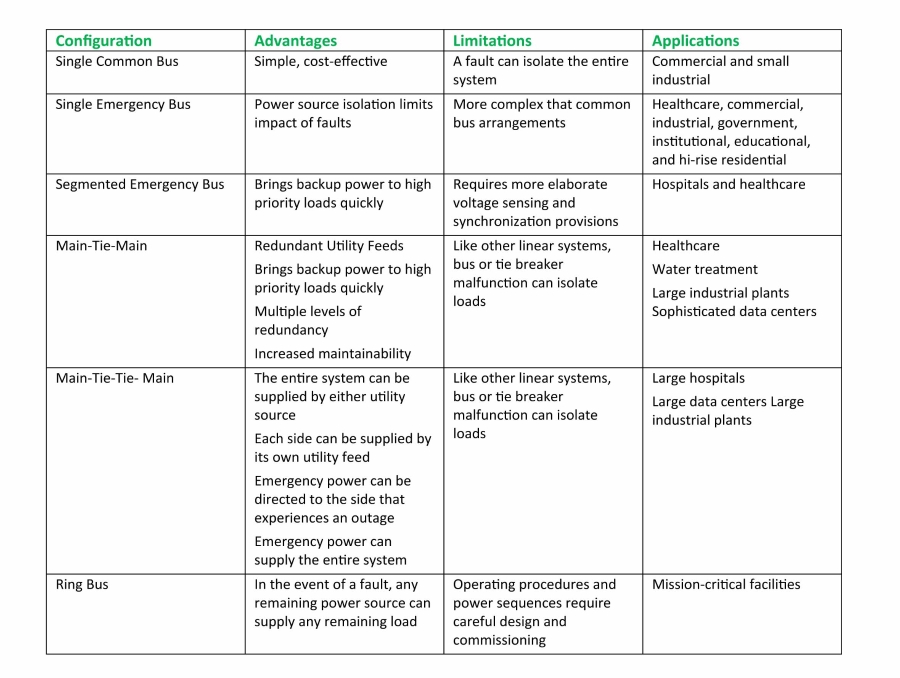
Using tie breakers and bus segments, backup power systems can be configured in a nearly infinite number of ways to meet a wide range of operational and redundancy objectives. The following sections provide samples of the most common types.
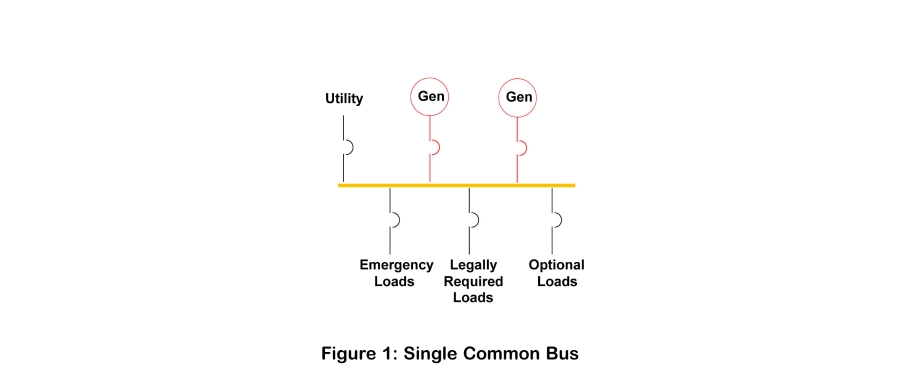
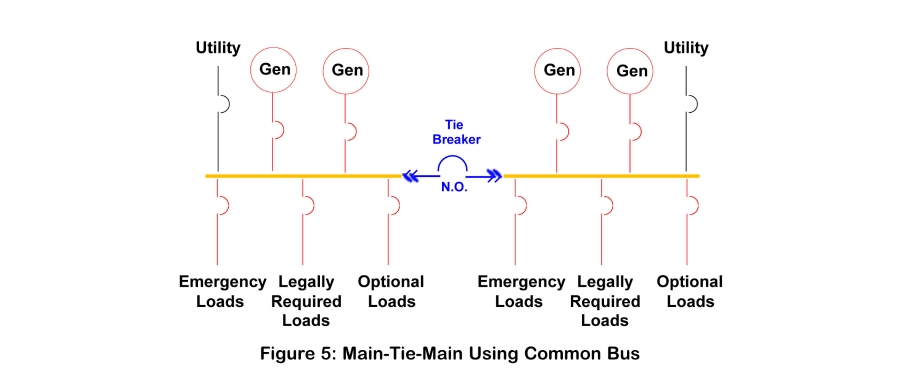
Single Common Bus
Common bus is the simplest configuration, where power sources and loads are all connected through a single bus. This arrangement is shown in Figure 1. When utility power fails, the utility breaker is opened, then the generators are started and the generator breakers close to provide backup power. Source and load management actions are completed using the circuit breakers shown.
Paralleling Switchgear Systems provide the highest levels of redundancy and maintainability for backup power applications. Understanding the function of tie breakers and electrical bus are key to optimizing backup power system configurations. The following sections describe tie breaker functions and provide examples of bus arrangements for a range of applications.
Overview of Breakers in Electrical Systems
Circuit breakers are used for multiple purposes in electrical systems. They are commonly used to connect electrical systems to power sources and to load circuits, and to protect people and equipment from overcurrents. On the source-side of electrical bus, generator breakers connect generators to electrical distribution bus, and utility main breakers connect electrical power feeds to bus. On the load side, distribution breakers connect and protect downstream loads, either directly or through automatic transfer switches.
A Tie Breaker is a type of circuit breaker that connects two sections of electrical bus serving different power sources. When closed, current can pass in either direction between them. As a result, they enable various arrangements for connecting power sources to loads, including paralleling two dissimilar power sources. Although this is most often the intent of the term tie breaker, it is also less formally used to identify breakers placed between two sections of bus.
Tie breakers are commonly applied to backup power systems in two ways. A Tie circuit breaker, such as a Utility Bus Tie or a Generator Bus Tie, connects similar power sources. Separately, a Generator Main Breaker ties a generator bus to a load bus. In this location, it can be used to transfer load between a utility source and a generator source. It can also be used to isolate elements of the system to deenergize it for maintenance and repair of devices and their components.
For additional information on the types of breakers used in power systems, see the ASCO Technical Brief entitled Nomenclature for Low-Voltage Circuit Breakers.
Types of Bus
Electrical bus is named for the type of equipment it connects. Common Bus connects both power source and load circuits. Generator Bus connects only generators together, and Utility Bus does the same for two or more utility feeds.
Common Arrangements
Using tie breakers and bus segments, backup power systems can be configured in a nearly infinite number of ways to meet a wide range of operational and redundancy objectives. The following sections provide samples of the most common types.
Single Common Bus
Common bus is the simplest configuration, where power sources and loads are all connected through a single bus. This arrangement is shown in Figure 1. When utility power fails, the utility breaker is opened, then the generators are started and the generator breakers close to provide backup power. Source and load management actions are completed using the circuit breakers shown.