Protective relays are sometimes used in backup power systems to protect circuits and load equipment from undesirable or potentially damaging electrical conditions and events. The following sections summarize their use in backup power systems and critical power equipment.
Protective Relay Overview
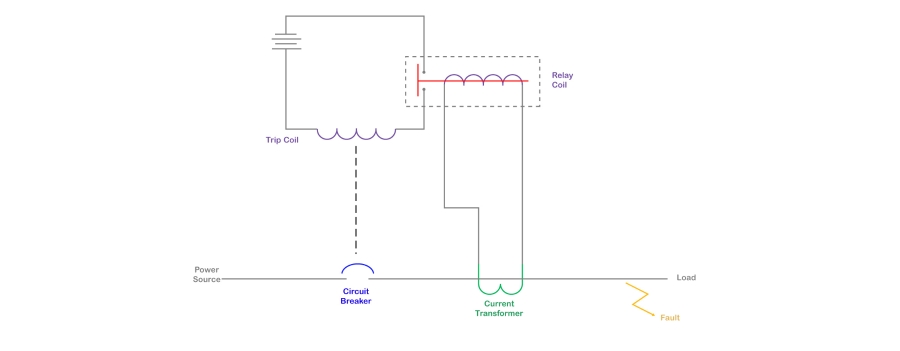
A protective relay compares inputs from an electrical sensing device against predetermined set points. When it detects an out-of-range condition, it signals another device to produce a responding action. For example, a protective relay may monitor current on a medium-voltage conductor using a current transformer; when the value of the current transformer output corresponds to an over-current condition, the protective relay will signal a circuit breaker to trip to protect downstream equipment. Such an arrangement is illustrated below.
Protective Relay Overview
A protective relay compares inputs from an electrical sensing device against predetermined set points. When it detects an out-of-range condition, it signals another device to produce a responding action. For example, a protective relay may monitor current on a medium-voltage conductor using a current transformer; when the value of the current transformer output corresponds to an over-current condition, the protective relay will signal a circuit breaker to trip to protect downstream equipment. Such an arrangement is illustrated below.